When we are learning scales in music you think that the scale having either happy sound(major scale) or sad sound(minor scale) but in reality many different sounds was created by these modes.In our carnatic music and hindustanic music there were many ragas. Each raga gives a type of feeling or music.As like that in Western music the modes were there which each mode create different type of music. These modes are also called scales.
Now we are seeing or taking a look at these other scales which are know as Musical modes.
what are modes in music ?
Modes,which are seven musical scales each with there own unique qualities and sounds.

The seven scales are all types of diatonic scales which means they have seven notes and two intervals that are half steps and five intervals that are whole steps.
There are seven types:
- Lonian mode
- Dorian mode
- Phrygian mode
- Lydian mode
- Mixolydian mode
- Aeolian mode
- locrian mode
These above modes can also be categorised into two types:
1.Major modes
- Lonian mode
- Lydian mode
- Mixolydian mode
2.Minor modes
- Dorian mode
- Phrygian mode
- Aeolian mode
- locrian mode
1.Lonion mode:
You most likely have already studied the lonion scale without knowing the lonion mode.How means It is same as Major scale.
Example: In C scale if we apply lonion mode then it is same as C major scale. So lonion mode is same as major scale.
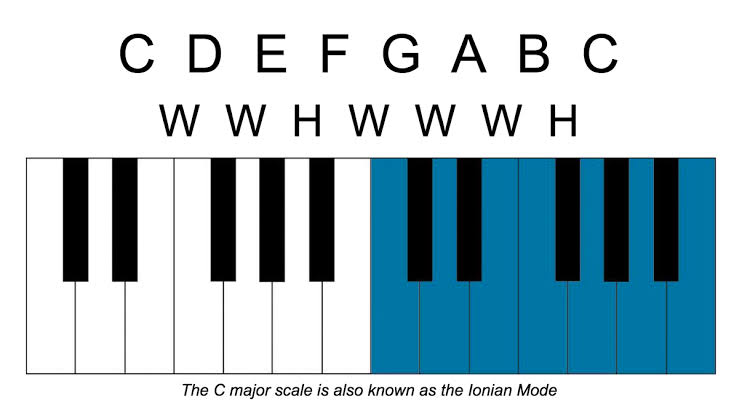
Formula of lonion mode
- W - whole note
- H - half note
2.Dorian mode:
It is type of Minor modes as it contains an interval of a minor third.It was called as karaharapriya ragam in carnatic music. It is same as natural minor scale but in this scale(mode) the sixth note of natural minor scale was half step raised.
Dorian Mode Formula
- W - whole note
- H - half note
Example: In C scale if we apply dorian mode below you can see root.
C D Eb F G A Bb C3.Phrygian mode:
It is very recognizable as it contains a minor second interval.This type of root was called as hanuma thodi ragam in carnatic music.It was same as natural minor scale but in this mode the second note of natural minor scale was half step down.
phrygian mode formula
- W - whole note
- H - half note
Example:In C scale if we apply phrygian mode below you can see the root.
C Db Eb F G Ab Bb C4.Lydian mode:
It was the one of the major mode.It was called as kalyani ragam in carnatic music. It was same as Major scale but in this mode the forth note of major scale was half step raised.
Lydian mode formula
- W - whole note
- H - half note
Example:In C scale if we apply Lydian mode below you can see the root.
CDEF#GABC5.Mixolydian mode:
Sometimes it is also called as dominant scale.It was major mode. It create a different sound. It was same as major scale but in this mode the seventh note of major scale was half step down.
Mixolydian mode formula
- W - whole note
- H - half note
Example:In C scale if we apply Mixolydian mode below you can see the root.
C D E F G A Bb C6.Aeolian mode:
As like lonian mode, this Aeolian mode also you studied without know this.How means it is same as minor scale there is no change. Aeolian mode is equal to minor scale.
Aeolian mode formula
- W - whole note
- H - half note
Example: In C scale if we apply Aeolian mode below you can see the root.
C D Eb F G Ab Bb C7.locrian mode:
It was the minor mode which is used very very few times. It is somtimes known as a half diminished scale. It was used in ghost sounds etc. It was formed by the moving half step down the second note and fifth note of the natural minor scale.
Locrian mode formula
- W - whole note
- H - half note
Example:In C scale if we apply locrian mode below you can see the root.
C Db Eb F Gb Ab Bb CFormulas of all musical modes
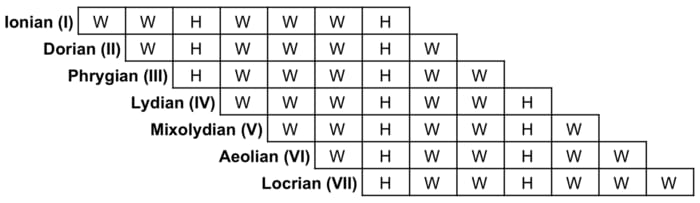
Note:
Dynamic Scales:Which scale have two semitone intervels(half steps) and five tone intervels(whole steps) within one Octave.
Whole Tone Scale:A whole tone scale is a hexatonic scale which means that it uses only six notes.These are only two type
C whole tone scale, B whole tone scale
